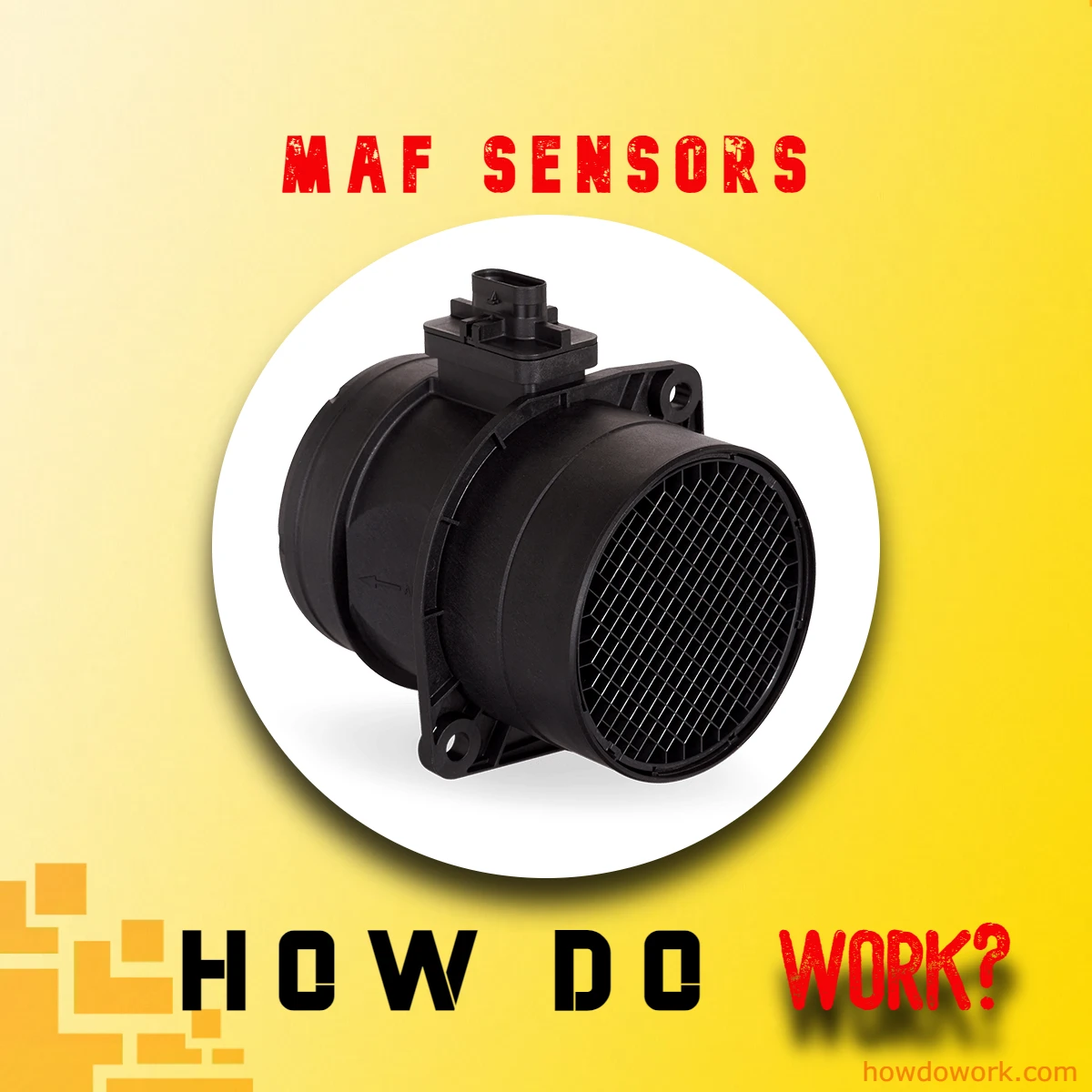
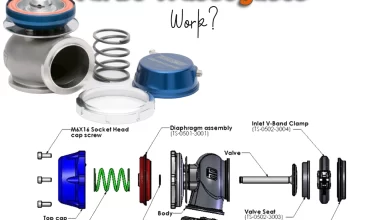
Mass Airflow Sensors (MAF sensors) are pivotal components in automotive engineering, tasked with a fundamental mission – measuring the mass of incoming air into an engine. These sensors operate on the principle of detecting changes in airflow, enabling them to precisely gauge the volume of air entering the engine’s intake system. This crucial data is then relayed to the engine control unit (ECU), allowing it to fine-tune the air-fuel mixture for combustion. The result is enhanced engine performance, improved fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions, making MAF sensors integral to the optimal functioning of modern vehicles.
| Feature | Hot Wire MAF Sensor | Vane Meter MAF Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Principle of Operation | Measures airflow by detecting changes in the electrical resistance of a heated wire. | Measures airflow by the rotation of a vane or paddlewheel in the airflow. |
| Measurement Precision | High precision, providing accurate airflow measurements. | Slightly less precise compared to hot wire sensors, especially at low airflow rates. |
| Sensitivity to Contaminants | Sensitive to contaminants like oil and debris that can accumulate on the heated wire, potentially affecting accuracy. | Less sensitive to contaminants, making them more robust in dirty or oily engine environments. |
| Response Time | Rapid response time due to the quick changes in wire resistance. | Slightly slower response time due to the rotational movement of the vane. |
| Common Use Cases | Often used in modern vehicles due to their high accuracy, suitable for precise fuel injection control. | Commonly found in older vehicles and some industrial applications. |
| Durability | Slightly less durable in the long term due to the sensitivity to contaminants. Regular cleaning may be required. | More durable in the presence of contaminants, requiring less frequent maintenance. |
| Cost | Generally, hot wire MAF sensors are more expensive due to their advanced technology. | Vane meter MAF sensors are typically more affordable. |
| Compatibility | Compatible with a wide range of vehicle makes and models. | Compatibility may be limited to certain vehicle types, especially older models. |
| Diagnostic Ease | Easier to diagnose issues as they often trigger specific trouble codes when malfunctioning. | Diagnosis may be less straightforward, as vane meter sensors may not always trigger specific codes. |
| Environmental Conditions | May be sensitive to extreme heat conditions, leading to potential overheating. | Tends to perform well in a variety of temperature conditions, including extreme cold. |
| Maintenance | Regular cleaning and maintenance may be necessary to ensure accuracy and prevent contamination-related issues. | Requires less frequent cleaning and maintenance, making them easier to manage. |
| Aftermarket Availability | Due to their common use in modern vehicles, hot wire MAF sensors are readily available in the aftermarket. | May be less commonly available in the aftermarket, especially for specific vehicle models. |
Contents
What are the maf sensors work?
In the realm of automotive engineering, the intricate dance of mechanical precision and electronic ingenuity often remains hidden beneath the sleek exteriors of our vehicles. Among the many unsung heroes of this technological symphony are Mass Airflow Sensors (MAF sensors). These unassuming components play a pivotal role in the orchestration of modern engines, performing a crucial task—measuring the mass of incoming air.
At their core, MAF sensors are emissaries of precision, delicately calibrated to detect even the subtlest nuances in the airflow that courses through your engine’s intake system. Their ability to measure this airflow with pinpoint accuracy lies at the heart of optimal engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emission control.
Now, let’s take a closer look at the inner workings of a MAF sensor, the different types available, and how they operate.
Types of MAF Sensors
MAF sensors come in various forms, but they all serve the same fundamental purpose: measuring incoming airflow to optimize engine performance. Two common types of MAF sensors are:
1. Hot Wire MAF Sensor
The hot wire MAF sensor is one of the oldest and most common types used in automotive applications. It operates based on the principle that as air flows over a heated wire, the wire’s resistance changes. Here’s how it works:
- A hot wire or hot film element is electrically heated to a constant temperature.
- As air flows into the intake system, it cools the heated wire.
- The rate of cooling is directly proportional to the mass of air passing over the wire.
- The sensor measures the wire’s resistance, which varies with the cooling rate, and converts it into an electrical signal.
- The ECU interprets this signal to determine the mass of incoming air and adjusts the fuel injection accordingly.
Hot wire MAF sensors offer precise measurements, making them popular in many vehicles. However, they can be sensitive to contaminants, like oil and debris, which may accumulate on the wire over time, affecting accuracy.
2. Vane Meter MAF Sensor
The vane meter MAF sensor, also known as a paddlewheel sensor, employs a different approach to measure airflow. Here’s how it operates:
- Inside the sensor housing, there’s a vane or paddlewheel positioned in the path of incoming air.
- As air flows over the vane, it causes it to spin.
- The speed of the vane’s rotation is directly proportional to the airflow’s mass.
- Sensors detect this rotational speed and convert it into an electrical signal.
- The ECU interprets the signal to determine the mass of air entering the engine, allowing for precise fuel injection control.
Vane meter MAF sensors are robust and less susceptible to contamination compared to hot wire sensors. However, they may not provide the same level of accuracy in measuring low airflow rates.
How MAF Sensors Work
Now that we’ve covered the basic types of MAF sensors, let’s delve into the nitty-gritty details of how these devices work their magic in your vehicle’s engine.
MAF sensors are positioned in the intake air duct, right before the throttle body. This strategic location allows them to measure the incoming air before it mixes with fuel and enters the combustion chamber. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how a MAF sensor operates:
- Airflow Measurement: As air is drawn into the engine through the intake system, it passes over or through the MAF sensor, depending on the type. This is the crucial moment when the MAF sensor gets to work.
- Sensor Output: The MAF sensor translates the measured airflow into an electrical signal. In the case of a hot wire sensor, it measures the change in resistance of the heated wire. For a vane meter sensor, it detects the rotational speed of the vane.
- Signal to the ECU: The electrical signal generated by the MAF sensor is sent to the engine control unit (ECU) or engine control module (ECM). This signal carries vital information about the mass of incoming air.
- Fuel Injection Adjustment: Armed with this data, the ECU makes real-time adjustments to the fuel injection system. It precisely calculates the amount of fuel required to achieve the optimal air-fuel ratio for combustion.
- Optimal Combustion: By maintaining the correct air-fuel mixture, the engine can achieve efficient combustion. This results in optimal power output, fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions.
- Constant Monitoring: MAF sensors continuously monitor airflow, ensuring that the engine adapts to changing driving conditions. Whether you’re idling at a stoplight or flooring the accelerator on the highway, the MAF sensor helps keep your engine running smoothly.
Importance of MAF Sensors
MAF sensors are not just another component in your vehicle’s engine; they are a critical part of the modern engine management system. Here’s why they are so important:
1. Fuel Efficiency
One of the primary benefits of MAF sensors is their role in optimizing fuel efficiency. By accurately measuring the mass of incoming air, the engine can precisely adjust the amount of fuel injected. This results in better mileage and cost savings at the pump.
2. Emission Control
In today’s environmentally conscious world, reducing harmful emissions is a top priority. MAF sensors play a key role in this by ensuring that the air-fuel mixture is at the optimal ratio for clean combustion. This leads to lower emissions of pollutants such as carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxides (NOx).
3. Engine Performance
Whether you’re a speed enthusiast or simply want a smooth, responsive ride, MAF sensors have you covered. They help maintain the right air-fuel ratio, which is essential for optimal engine performance. This translates to better acceleration, smoother idling, and overall improved engine responsiveness.
4. Diagnostics
When an issue arises in your vehicle’s engine, the onboard diagnostics system relies on data from the MAF sensor to pinpoint the problem. Whether it’s a clogged air filter or a malfunctioning sensor itself, having accurate data from the MAF sensor aids in quicker and more precise troubleshooting.
Why do maf sensors fail?
Mass Airflow Sensors (MAF sensors) are critical components in modern automotive engines, responsible for measuring the mass of incoming air and providing data to the engine control unit (ECU) to adjust the air-fuel mixture. However, like any electronic or mechanical part, MAF sensors can fail over time. Here are some common reasons why MAF sensors may fail:
- Contamination: MAF sensors are exposed to the airstream entering the engine. Over time, contaminants like dust, oil mist, and debris can accumulate on the sensor’s elements or vane (depending on the sensor type). This buildup can disrupt the sensor’s ability to accurately measure airflow.
- Wear and Tear: MAF sensors have moving parts, especially in vane meter-type sensors. Continuous use and exposure to varying temperatures can lead to wear and tear, affecting the sensor’s performance.
- Age: Like all components, MAF sensors can simply wear out with age. The internal components may deteriorate, leading to inaccurate readings or sensor failure.
- Physical Damage: Any physical damage to the sensor, such as cracked housing, bent wires, or damaged connectors, can impair its functionality.
- Electrical Issues: Wiring harnesses that connect the MAF sensor to the ECU may develop issues, such as loose connections, frayed wires, or corrosion. These problems can disrupt the flow of data between the sensor and the ECU.
- Excessive Heat or Cold: Extreme temperature conditions can impact sensor performance. Extremely hot conditions can lead to sensor overheating, while extreme cold can affect the sensor’s ability to function properly.
- Improper Cleaning: While cleaning a contaminated MAF sensor can extend its life, improper cleaning methods or the use of unsuitable cleaning agents can damage delicate sensor components.
- Manufacturer Defects: In rare cases, MAF sensors may have manufacturing defects that cause them to fail prematurely.
- Poor Air Filtration: A clogged or dirty air filter can lead to increased levels of contaminants reaching the MAF sensor, accelerating its wear and reducing its lifespan.
- Fuel Additives and Oil Mist: Some engine treatments or fuel additives can create oil mist in the intake system, which can adhere to the MAF sensor elements and affect its accuracy.
When a MAF sensor fails, it can lead to a range of issues such as poor engine performance, decreased fuel efficiency, rough idling, and even an illuminated check engine light (CEL). Diagnosing and addressing MAF sensor problems promptly through cleaning or replacement is essential to ensure optimal engine operation and vehicle performan
MAF Sensor Maintenance and Common Issues
While MAF sensors are crucial for your vehicle’s performance, they are not immune to issues. Routine maintenance and awareness of common problems can help ensure your MAF sensor continues to do its job effectively.
Maintenance Tips
- Air Filter Replacement: A clean air filter ensures that the MAF sensor receives clean, debris-free air. Regularly inspect and replace the air filter as recommended by your vehicle’s manufacturer.
- Cleaning: In the case of hot wire MAF sensors, cleaning may be necessary if contaminants build up on the sensor element. Use a specialized MAF sensor cleaner to avoid damaging the delicate components.
- Visual Inspection: Periodically inspect the MAF sensor for signs of physical damage, such as loose wires or sensor housing cracks. Address any issues promptly to prevent further damage.
Common Issues
- Contamination: Both hot wire and vane meter MAF sensors can become contaminated over time, affecting their accuracy. Contaminants like dust, oil, and debris can accumulate on the sensor element or vane, leading to skewed readings.
- Sensor Failure: Like any electronic component, MAF sensors can fail due to age or manufacturing defects. When a MAF sensor fails, it can result in poor engine performance, rough idling, and decreased fuel efficiency.
- Wiring Problems: Wiring harnesses connecting the MAF sensor to the ECU can develop faults or become damaged. This can disrupt the flow of data between the sensor and the ECU, leading to issues.
- Incorrect Installation: During maintenance or repairs, improper installation of the MAF sensor can lead to inaccurate readings. It’s essential to follow manufacturer guidelines when replacing or cleaning the sensor.
MAF Sensor Troubleshooting and Replacement
In the world of automotive maintenance and repair, troubleshooting and replacing a Mass Airflow Sensor (MAF sensor) can be a common task. Just like any other component in your vehicle, MAF sensors can experience issues over time. In this section, we’ll dive deeper into how to diagnose MAF sensor problems and the steps involved in replacing one.
Diagnosing MAF Sensor Issues
Detecting problems with your MAF sensor is crucial to maintaining your vehicle’s optimal performance. Here are some common symptoms that may indicate a malfunctioning MAF sensor:
1. Poor Acceleration and Power Loss
If your vehicle is sluggish during acceleration or lacks power, a faulty MAF sensor could be to blame. The sensor’s inaccurate readings may lead to an improper air-fuel mixture, resulting in reduced engine performance.
2. Rough Idling
A malfunctioning MAF sensor can cause your engine to idle roughly or even stall when you come to a stop. This is because the sensor’s incorrect data can disrupt the engine’s ability to maintain a stable idle speed.
3. Decreased Fuel Efficiency
A drop in fuel efficiency can be a sign of MAF sensor issues. When the sensor fails to provide accurate data, the engine may consume more fuel than necessary due to an improper air-fuel mixture.
4. Illuminated Check Engine Light
Modern vehicles are equipped with onboard diagnostics systems that can detect MAF sensor problems. If the check engine light (CEL) is illuminated on your dashboard, it’s advisable to have the vehicle’s computer scanned for trouble codes. A MAF sensor-related code, such as P0100, P0101, or P0102, may indicate an issue with the sensor.
Troubleshooting Steps
If you suspect a problem with your MAF sensor based on the symptoms mentioned above, here’s a step-by-step guide to help you troubleshoot the issue:
1. Check for Visual Damage
Start by inspecting the MAF sensor visually. Look for loose wires, damaged connectors, or cracks in the sensor housing. Any physical damage could contribute to sensor malfunction.
2. Clean the MAF Sensor
In the case of a hot wire MAF sensor, contaminants like dust, oil, and debris can accumulate on the sensor element, affecting its accuracy. You can try cleaning the MAF sensor using a specialized MAF sensor cleaner. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully to avoid damaging sensitive components.
3. Inspect Wiring and Connectors
Ensure that the wiring harness connecting the MAF sensor to the engine control unit (ECU) is intact and properly connected. Wiring issues can disrupt the flow of data between the sensor and the ECU.
4. Scan for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
If you have access to a vehicle diagnostic tool or visit an auto repair shop, scan the vehicle’s computer for trouble codes. A MAF sensor-related code will provide valuable information about the nature of the problem.
5. Perform Voltage and Resistance Tests
For more advanced troubleshooting, you can perform voltage and resistance tests on the MAF sensor. This typically requires a multimeter and access to your vehicle’s service manual for specific testing procedures.
Replacing a MAF Sensor
If troubleshooting indicates that your MAF sensor is indeed faulty and needs replacement, follow these steps to ensure a successful replacement:
1. Gather Tools and Parts
Before starting, make sure you have the necessary tools and a replacement MAF sensor. Refer to your vehicle’s service manual for the correct part number and specifications.
2. Disconnect the Battery
To ensure safety and prevent electrical damage, disconnect the vehicle’s battery.
3. Locate the MAF Sensor
The MAF sensor is typically located in the intake air duct, near the air filter housing. Refer to your vehicle’s service manual for the exact location.
4. Remove the Old MAF Sensor
Depending on your vehicle, you may need to remove retaining clips, screws, or clamps holding the sensor in place. Carefully detach the sensor from the air duct.
5. Disconnect Wiring
Unplug the wiring harness connector from the old MAF sensor.
6. Install the New MAF Sensor
Connect the wiring harness to the new MAF sensor and secure it in place using the appropriate fasteners.
7. Reconnect the Battery
Reconnect the vehicle’s battery to restore power.
8. Clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes
If the check engine light was illuminated due to the MAF sensor issue, use a diagnostic tool to clear the trouble codes from the vehicle’s computer.
9. Test Drive
Take your vehicle for a test drive to ensure that the symptoms associated with the old MAF sensor have been resolved.
Replacing a MAF sensor can vary in complexity depending on your vehicle’s make and model. If you’re unsure or uncomfortable with the process, it’s always a good idea to seek assistance from a qualified mechanic or automotive technician.
Reviewing the Latest MAF Sensor Technology
In a world where precision and efficiency reign supreme, this latest MAF sensor model proves to be a noteworthy addition to the realm of engine management systems. Let’s take a closer look at what sets this technology apart.
Precision Redefined
The first thing that struck me about this latest MAF sensor is its unparalleled precision. In the world of engine management, precision is paramount, and this sensor certainly doesn’t disappoint. It takes the measurement of incoming air to a whole new level.
One of the standout features is its ability to measure airflow with remarkable accuracy. Whether you’re idling in traffic or pushing your vehicle to its limits on the open road, this MAF sensor ensures that the engine control unit (ECU) receives data of the highest fidelity. This precision translates into optimal air-fuel mixture control, resulting in improved fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and enhanced engine performance.
Versatility in Design
Innovation extends beyond just precision; it’s also about adaptability. This MAF sensor showcases a design that seamlessly fits into a wide range of automotive applications. Its versatility allows it to be integrated into various intake systems, making it a practical choice for different vehicle makes and models.
The sensor’s ability to function effectively in diverse conditions is truly impressive. From scorching summer days to frigid winter nights, it maintains its performance integrity. This robustness ensures that drivers can rely on consistent engine performance, regardless of the weather or driving conditions.
Advanced Data Integration
In an era where connectivity and data are king, this MAF sensor doesn’t fall behind. It boasts advanced data integration capabilities that allow it to communicate seamlessly with the vehicle’s onboard computer systems. This means that it not only measures airflow with unparalleled precision but also shares this data in real-time with the ECU.
The result is a dynamic engine management system that can adapt instantaneously to changing driving conditions. Whether you’re cruising on the highway, towing a heavy load, or navigating through city traffic, the ECU receives the information it needs to optimize the air-fuel mixture and ensure smooth engine operation.
Durability and Longevity
Durability is another feather in the cap of this MAF sensor. It’s constructed with high-quality materials and built to withstand the rigors of the road. This means fewer replacements and greater peace of mind for vehicle owners.
Moreover, its longevity is a testament to its engineering. It continues to perform consistently even after prolonged use, making it a cost-effective investment for car owners in the long run.
Conclusion: A Technological Triumph
In conclusion, the latest MAF sensor model under review is a technological triumph that exemplifies the ongoing evolution of automotive precision and efficiency. Its precision, versatility, advanced data integration, durability, and longevity collectively redefine what we can expect from MAF sensors in the modern automotive landscape.
This sensor isn’t just a component; it’s an enabler of superior engine performance, enhanced fuel efficiency, and reduced environmental impact. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, an environmentally conscious driver, or simply someone who values the optimal functioning of their vehicle, this MAF sensor is undoubtedly a game-changer. It’s a testament to the boundless potential of technology to elevate the driving experience.
FAQs
A Mass Airflow Sensor (MAF sensor) is an essential component in modern vehicles. Its primary function is to measure the mass of incoming air that enters the engine’s intake system. This data is crucial because it allows the engine control unit (ECU) to adjust the air-fuel mixture, ensuring optimal combustion, engine performance, fuel efficiency, and reduced emissions.
MAF sensors use different methods depending on the type. The two common types are hot wire and vane meter sensors. Hot wire sensors measure airflow by detecting changes in the electrical resistance of a heated wire as air flows over it. Vane meter sensors, on the other hand, measure airflow by the rotation of a vane or paddlewheel in the airflow.
MAF sensors can fail due to various reasons, including contamination (accumulation of dust, oil, or debris on the sensor), wear and tear, age, physical damage, electrical issues, extreme temperature conditions, and manufacturing defects.
Common symptoms of a failing MAF sensor include poor acceleration, power loss, rough idling, decreased fuel efficiency, and an illuminated check engine light (CEL). These symptoms often result from inaccurate airflow measurements.
In some cases, yes. Hot wire MAF sensors can be cleaned with specialized MAF sensor cleaner to remove contaminants. However, vane meter sensors are less sensitive to contaminants and may require less frequent cleaning. If cleaning doesn’t resolve the issue, replacement is often necessary.
No, there are different types of MAF sensors, and they can vary in terms of precision, sensitivity to contaminants, response time, and compatibility with specific vehicle makes and models. Hot wire sensors are known for their high precision, while vane meter sensors are more robust but slightly less precise.
Diagnosing a MAF sensor problem may involve visual inspection for physical damage, checking the wiring and connectors, using a diagnostic tool to scan for trouble codes, and performing voltage and resistance tests. An illuminated check engine light (CEL) may also indicate a MAF sensor issue.
Replacing a MAF sensor can be a DIY task, depending on your mechanical skills and the accessibility of the sensor in your vehicle. It’s essential to follow your vehicle’s service manual and take necessary safety precautions. If you’re uncertain, seeking professional assistance is advisable.
Yes, aftermarket MAF sensors are available for many vehicle makes and models. However, it’s crucial to choose a reputable brand to ensure quality and compatibility with your vehicle.
The frequency of cleaning or replacement depends on various factors, including driving conditions and environmental factors. It’s a good practice to consult your vehicle’s maintenance schedule and service manual for specific recommendations.
Read More: